Permeation Grouting
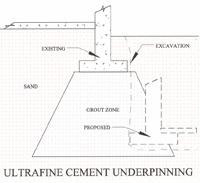
Permeation grouting is probably the most prevalent method used to shore up or stiffen a volume of soil that needs to support a new set of loads in support of construction or renovation. It is the injection of grout at low pressures into the soil matrix to permeate or encapsulate the individual soil grains without otherwise disturbing the natural state of the soil or increasing its volume. It is a highly cost-effective alternative to conventional shoring systems.
Permeation grouting method is used to improve a specific soil’s ability to bear loads by reducing its permeability, its cohesion, the makeup of the soil, or a combination of these outcomes.
The technology involves placing a series of sleeve pipes in drilled holes that intersect the soil mass to be stabilized and stiffened. The sleeves are designed as one-way valves, keeping soil fluids outside the pipe but allowing the grouting mixture to get out. Grout is pumped through the sleeves into the soil under pressure. This is low but steady pressure, as our mission is to permeate the spaces between the soil grains, not fracture the material.


Each soil situation is different, so we create a customized solution for each construction site. We must strike the right mix to account for soil type, degree of soil compaction (current and desired), grain size distribution, gel time, grout rheology, equipment placement and proper pump pressure.
FSS, Inc. has completed numerous soil permeation grouting projects. We utilize the latest state-of-the-art cement grouts, microfine cement grouts, sodium silicate grouts, acrylate grouts and polyurethane grouts.
PERMEATION GROUTING CAN BE USED TO:
- Stiffen soil that is destined to carry increased loads
- Shore up foundations subject to adjacent construction projects
- Prevent undermining of structures during excavation or tunneling
- Strengthen sands and gravels
- Repair structural and rock formations
- Stop the flow of groundwater

